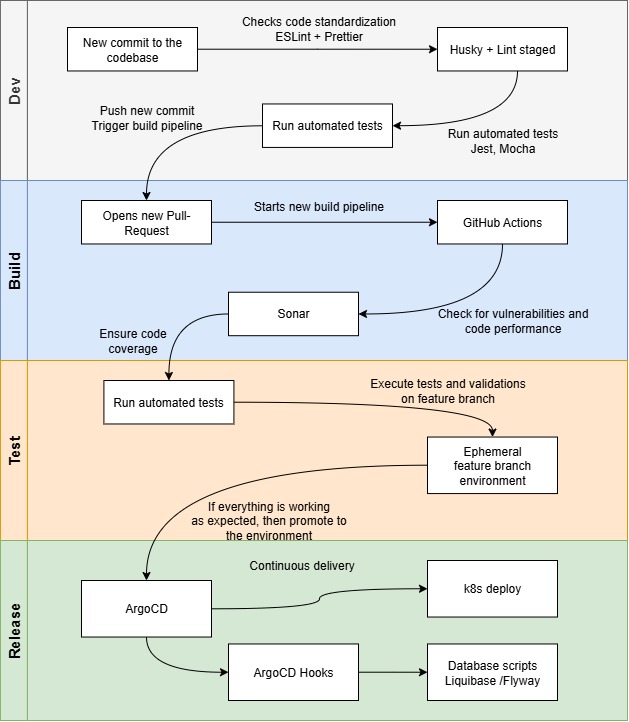
CI/CD Workflow
1. CD/CD workflow diagram
2. CI/CD Pipeline with GitHub Actions, SonarQube, and ArgoCD
2.1. Source Code Management & Trigger
-
Use GitHub as the single source of truth.
-
Commits or pull requests trigger the CI/CD pipeline automatically via GitHub Actions.
2.2. Continuous Integration (CI) with GitHub Actions
-
Automated build of the application and container image.
-
Run unit tests, integration tests, and linting.
-
Build artifacts (Docker images) are stored in a container registry.
2.3. Code Quality & Security with SonarQube
-
Integrate SonarQube in the CI workflow to perform static code analysis.
-
Detect bugs, code smells, security vulnerabilities, and maintain code quality standards.
-
Fail the build if quality gates are not met, ensuring only high-quality code progresses to deployment.
2.4. Continuous Deployment (CD) with ArgoCD
-
ArgoCD continuously monitors Git repositories for updated Kubernetes manifests or Helm charts.
-
Automatically deploys the new release to the target Kubernetes cluster once the CI pipeline completes successfully.
-
Supports declarative GitOps model, rollback on failure, and progressive rollout strategies.
2.5. Horizontal Scalability & Reliability
-
CI/CD flow ensures consistent and repeatable deployments.
-
Combined with Kubernetes features (autoscaling, node pools), new releases can scale horizontally without downtime.
2.6. Observability & Feedback Loop
-
Provide real-time feedback via GitHub Actions status checks.
-
Logs and metrics from ArgoCD help monitor deployment health and performance post-release.
3. Developer Experience Tooling for Consistent and High-Quality Codebase
3.1. Pre-commit Hooks with Husky + Lint-Staged
-
Automatically enforce code quality before commits.
-
Run linters, formatters, or tests only on staged files, preventing broken or inconsistent code from entering the repository.
-
Reduces human error and ensures team-wide adherence to standards.
3.2. Code Quality and Formatting: ESLint + Prettier
-
ESLint enforces consistent coding patterns and identifies potential bugs.
-
Prettier ensures a unified code style across the codebase.
-
Together, they reduce code review overhead and maintain readability.
3.3. Unit and Integration Testing with Jest
-
Provides a robust framework for writing and running automated tests.
-
Ensures that individual modules and their integrations behave as expected.
-
Critical for maintaining confidence during refactors or feature additions.
3.4. Environment-aware Testing with Testcontainers
-
Allows running ephemeral, isolated containerized dependencies (like databases) for tests.
-
Ensures test environments closely resemble production, reducing environment-related bugs.
3.5. Type Safety with TypeScript
-
Enforces static typing across the codebase.
-
Helps catch errors at compile time rather than runtime.
-
Enhances developer productivity and reduces bugs in large, complex applications.